What is a CV Axle Shaft
Learn all about CV axle shafts with our comprehensive guide, covering everything from CV axle components, working principle and various types of CV axle.
A CV (constant velocity) axle shaft, also known as a half shaft, is a component of a vehicle's drivetrain that delivers torque (rotational force) from the transmission or differential to the wheels, allowing the vehicle to move forward or backward. The CV axle shaft is typically found on front-wheel drive vehicles, and it connects the front wheels to the transmission or differential.
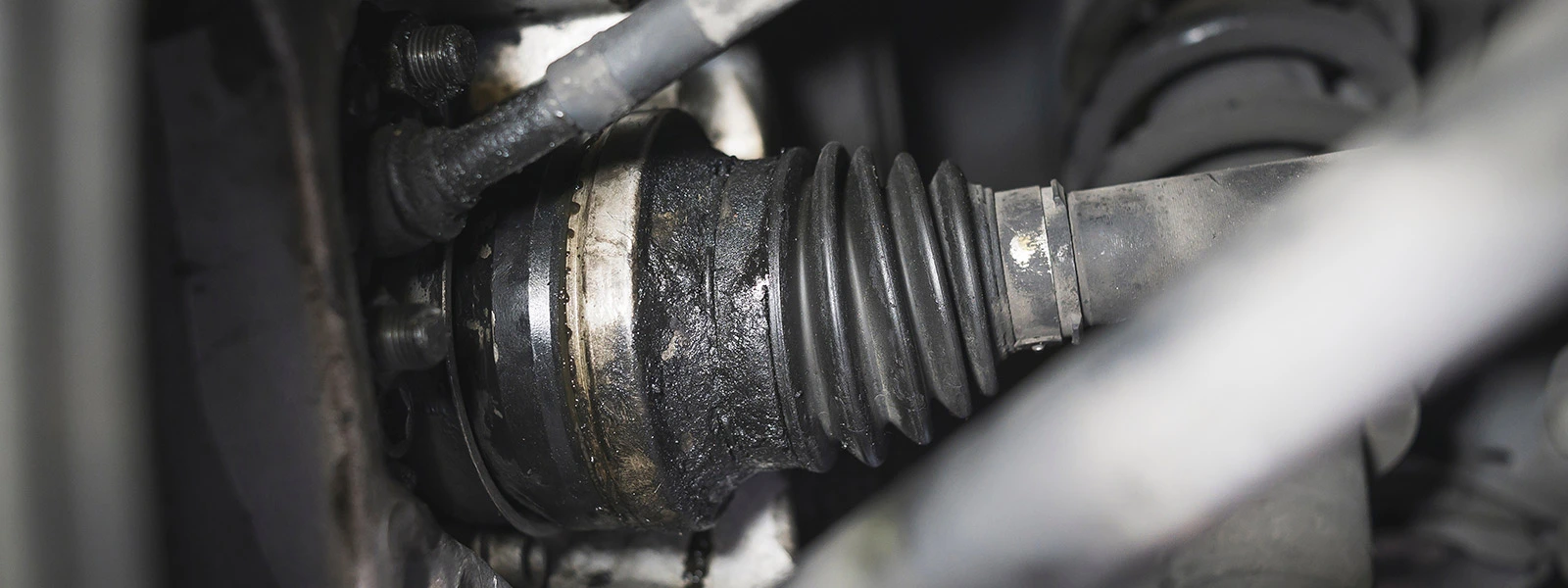

Why CV axle shaft is important in a vehicle
As mentioned, as a crucial component of a car's drivetrain, a CV axle shaft connects the engine's power to the wheels, allowing the car to move smoothly and safely.
- Power transmission. The CV axle shaft transfers the power from the engine and the transmission to the wheels. Without the CV axle shaft, the car would not be able to move.
- Smooth operation. The CV joints allow the axle to flex and rotate while maintaining a constant velocity, which results in smooth and efficient operation of the vehicle.
- Handling. The CV axle shaft is responsible for transmitting power to the wheels while also allowing them to turn and move the vehicle. This helps the car to handle better and provides stability while driving.
- Safety. A damaged CV axle shaft can cause vibrations, noise, and even a loss of control while driving. Regular maintenance and replacement of worn or damaged CV axle shafts can help ensure the safety of the vehicle and its passengers.
Understanding the parts of CV axle
Technically, a CV axle shaft consists of these components:
Inner CV joint: The inner joint is located at the end of the axle shaft closest to the transmission. It connects to the transmission output shaft and allows the axle to rotate with the engine and transmission while also allowing for the up and down movement of the suspension.
Outer CV joint: Outer CV joint is located at the end of the axle shaft closest to the wheel hub. It connects to the wheel hub and allows the axle to transfer power to the wheel while also allowing for the steering movements of the wheel.
Boot: The CV joints are protected by a rubber or plastic boot that covers the joint and prevents dirt, water, and debris from getting in. The boot is filled with grease that lubricates the joint and aims to reduce wear and tear.
Shaft: The shaft is the long metal rod that connects the inner and outer CV joints. It is made from high-strength steel and is designed to withstand the forces generated by the engine and transmission.
Bearings: The CV joints have bearings that support the axle and allow it to rotate smoothly. These bearings are usually sealed to prevent dirt and water from entering and causing damage.
Splines: The shaft has splines on each end that allow it to slide into the transmission and wheel hub. The splines are designed to transfer torque from the transmission to the wheels and are machined to precise specifications to ensure a secure connection.
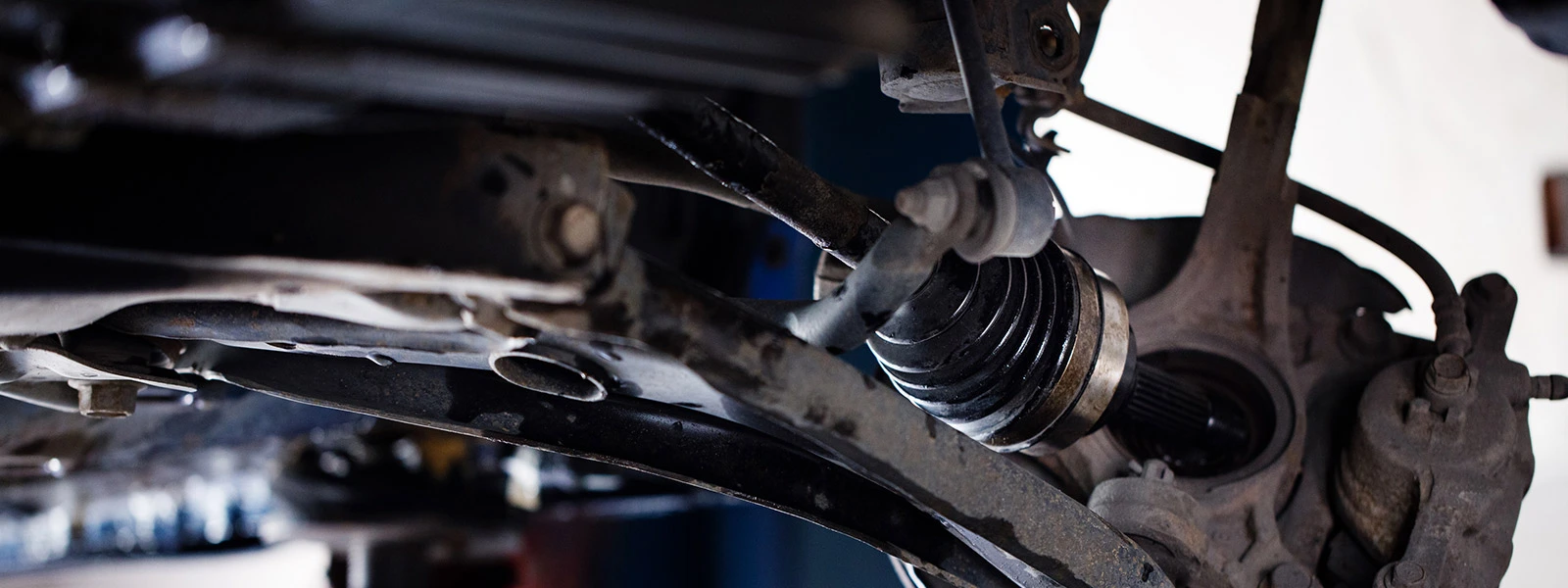
How does a CV axle work?
The CV axle works by transferring torque from the transmission or differential to the wheels while allowing them to move independently of each other. The axle consists of a shaft with two constant velocity joints (CV joints) at each end. The inner CV joint is connected to the transmission or differential, while the outer CV joint is connected to the wheel hub. The CV joints are designed to maintain a constant velocity, even when the axle is turning at different angles. This allows the vehicle to maintain a smooth and stable ride, without experiencing any vibration or jerking.
The CV joints consist of an inner race, an outer race, and a cage with bearings. The bearings allow the joint to rotate smoothly while transmitting torque from the axle to the wheel. The joint is enclosed in a protective boot that keeps dirt and debris out while retaining the grease inside the joint. As the vehicle moves, the CV axle rotates, and the CV joints allow the axle to flex and rotate while maintaining a constant velocity. This allows the wheels to turn independently of each other, which is essential for cornering, steering, and suspension movement.

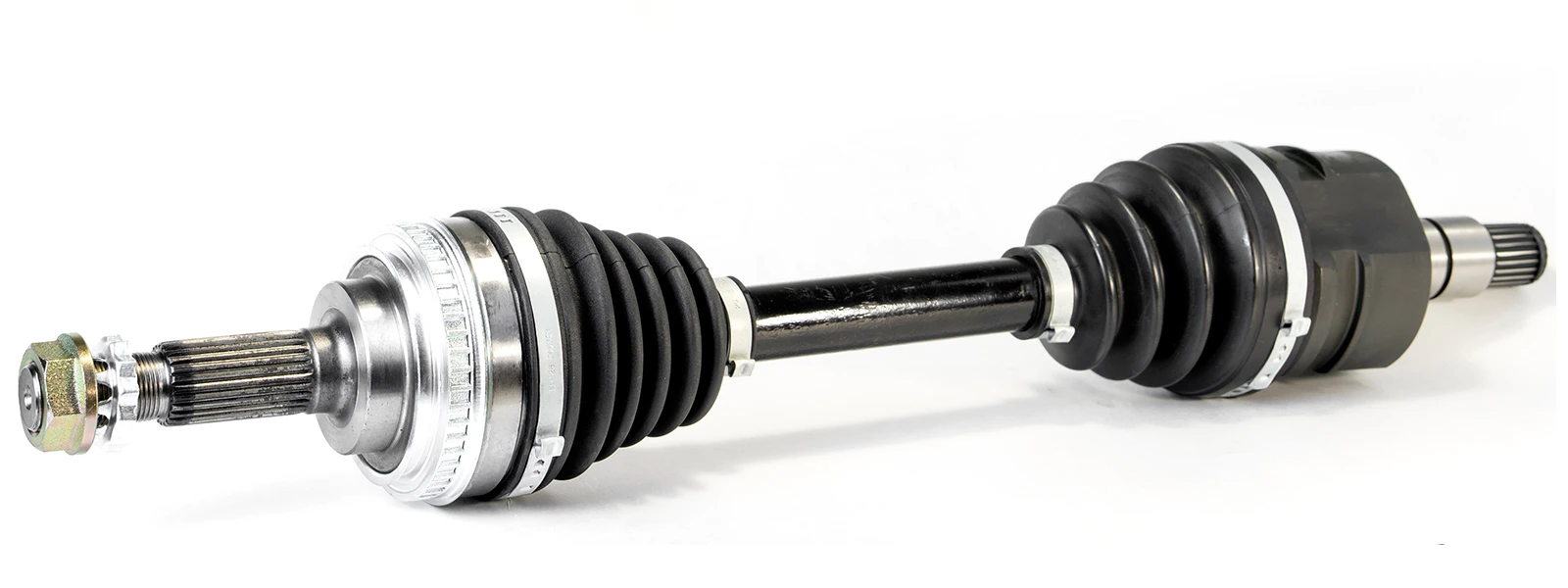
Different Types of CV axle shaft
Based on different classification factors, CV axle shaft can be divided into various types. For example, here are the types of CV axle shafts classified by the installing position:
- Front Left Driver Side (FLDS) CV Axle Shaft: This type of CV axle shaft is installed on the left side of the vehicle's front suspension system, from the transaxle to the front left wheel hub. It transmits power to the left front wheel and is designed to handle the load and torque applied during acceleration and cornering.
- Front Right Passenger Side (FRPS) CV Axle Shaft: This type of CV axle shaft is installed on the right side of the vehicle's front suspension system, from the transaxle to the front right wheel hub. It transmits power to the right front wheel and is designed to handle the load and torque applied during acceleration and cornering.
- Rear Left Driver Side (RLDS) CV Axle Shaft: This type of CV axle shaft is installed on the left side of the vehicle's rear suspension system, from the differential to the left rear wheel hub. It transmits power to the left rear wheel and is designed to handle the load and torque applied during acceleration and cornering.
- Rear Right Passenger Side (RRPS) CV Axle Shaft: This type of CV axle shaft is installed on the right side of the vehicle's rear suspension system, from the differential to the right rear wheel hub. It transmits power to the right rear wheel and is designed to handle the load and torque applied during acceleration and cornering.

And when classified by type of vehicle and the position of the axle, the breakdown of the classification for each type will be:
- Front-Wheel Drive (FWD) Axle Shaft: This type of CV axle shaft is typically used in front-wheel drive vehicles. It connects the transaxle to the front wheel hub and is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the wheels. FWD axle shafts usually have two CV joints, one at each end.
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD) Axle Shaft: RWD axle shafts are found in rear-wheel drive vehicles and are responsible for transferring power from the differential to the rear wheels. They typically have one CV joint on each end and may also have a universal joint (U-joint) to allow for flexing of the driveshaft.
- All-Wheel Drive (AWD) Axle Shaft: AWD vehicles use a combination of FWD and RWD axle shafts to provide power to all four wheels. AWD axle shafts can vary in design depending on the specific system, but they usually have multiple CV joints and may use a center differential to distribute power between the front and rear axles.
- Constant Velocity (CV) Axle Shaft: CV axle shafts are used in both FWD and AWD vehicles and have a unique design that allows for smooth power transfer even when the wheels are turning at different speeds. They use a series of articulated joints (CV joints) to maintain a constant velocity between the transmission and the wheels.
- Half-Shaft Axle: A half-shaft axle is a shorter version of a CV axle shaft and is commonly used in FWD vehicles with independent rear suspension. It connects the transaxle to the rear wheel hub and typically has only one CV joint.
As a professional and full-fledged auto parts supplier from China, A-Premium is always devoted to providing the top quality CV axle shaft to all the customers. We have various types of CV shafts to meet your needs. Contact us now!

